Introduction
A mastectomy can be life changing, both physically and emotionally. For many women, restoring breast shape becomes an important part of recovery. Mastectomy reconstruction offers several pathways depending on personal goals, anatomy and medical history. Understanding how the process works helps patients feel more prepared and informed. Reconstruction is not a single procedure but a carefully planned journey tailored to each individual.
Understanding the Purpose of Mastectomy Reconstruction
Mastectomy reconstruction aims to recreate breast shape following removal of breast tissue. The goal is not only aesthetic restoration but also physical balance. Rebuilding volume can help clothing fit more comfortably and restore symmetry across the chest. Some women choose reconstruction immediately, while others prefer to wait. The decision depends on treatment plans, healing and personal readiness. Modern mastectomy reconstruction focuses on achieving natural contour and proportion rather than simply replacing volume.
Timing: Immediate vs Delayed Reconstruction
One of the first decisions involves timing. Immediate reconstruction after mastectomy takes place during the same operation as the mastectomy. This approach preserves much of the natural breast skin and can reduce the number of surgeries overall. Delayed reconstruction occurs months or even years later, often after additional treatments have concluded. Both approaches are medically sound. The choice depends on overall health, recovery plans and personal preference. Careful consultation helps determine which timing aligns best with individual circumstances.
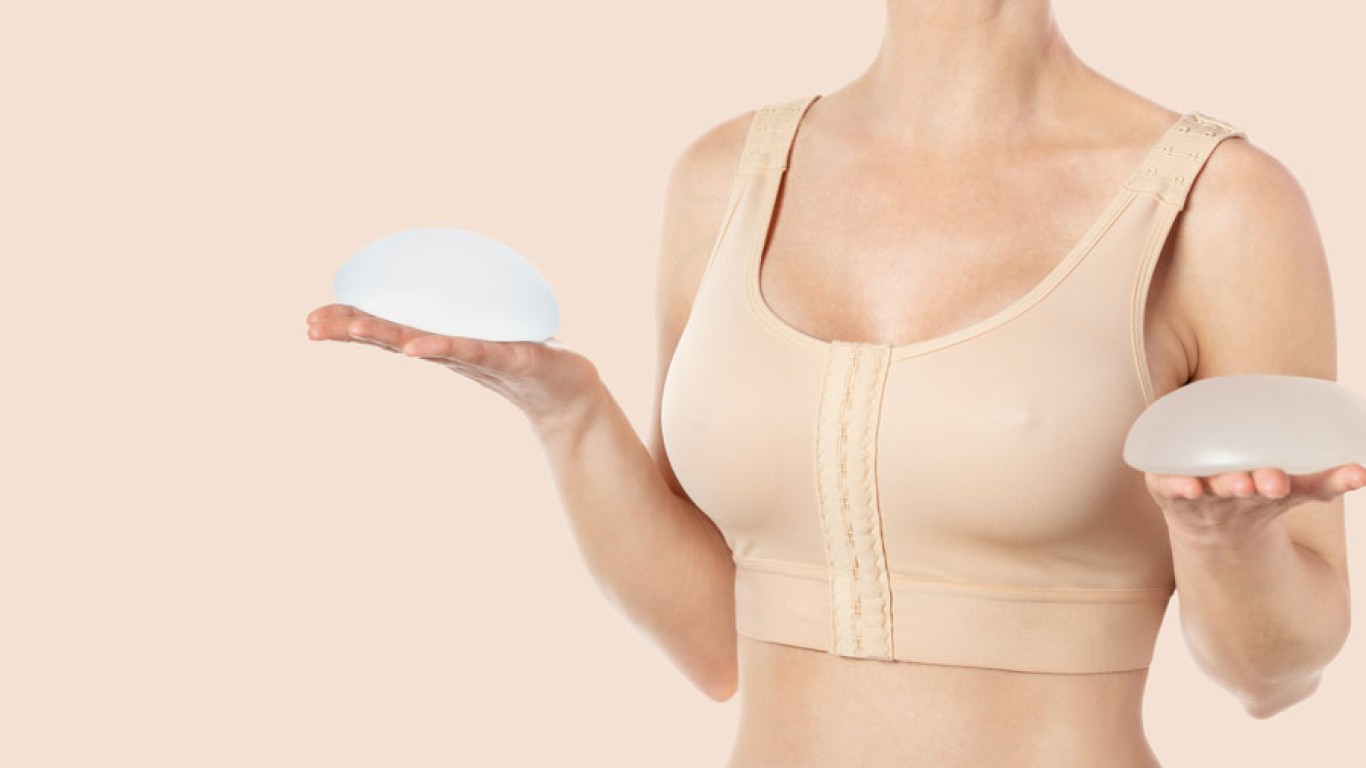
Implant Based Mastectomy Reconstruction
Implant reconstruction is one of the most common options. It involves placing a silicone implant beneath the chest muscle or skin. In some cases, a temporary tissue expander is inserted first to gradually stretch the skin. Once the desired space is created, a permanent implant replaces the expander. This method provides predictable volume and shape. Implant based reconstruction after mastectomy often involves shorter operative time compared to tissue flap procedures. Many patients appreciate the structured contour it provides.
Autologous Tissue Reconstruction
Autologous reconstruction uses the patient’s own tissue to rebuild the breast. Tissue is usually taken from the abdomen, back or thighs. This approach creates a softer, more natural feel because the material is living tissue. Procedures such as DIEP or latissimus dorsi flap reconstruction fall into this category. Mastectomy reconstruction using autologous tissue may involve longer surgery and recovery. However, many patients value the organic appearance and long term integration.

Combining Implants with Tissue Techniques
In some cases, a hybrid approach offers the best outcome. Surgeons may use both implants and fat grafting to refine contour. Fat transfer helps soften edges and improve symmetry. This layered technique enhances shape while maintaining structural support. Mastectomy reconstruction today often includes these combined strategies for optimal balance. The aim is to tailor volume and projection carefully rather than rely on one method alone.
Nipple and Areola Mastectomy Reconstruction
Restoring the nipple and areola is often the final stage. This step may involve minor surgical reshaping or medical tattooing. The objective is to recreate natural pigmentation and projection. Although small in scale, this stage can significantly influence overall appearance. Mastectomy reconstruction is considered complete when contour and detailing feel cohesive. Attention to these finishing touches contributes to emotional closure for many women.
Mastectomy Reconstruction Recovery and Healing Process
Recovery varies depending on the chosen technique. Implant procedures typically involve shorter hospital stays. Tissue flap surgeries may require more extended monitoring. Swelling and tightness are common in early stages. Over time, the reconstructed breast settles into a more natural shape. Follow up appointments ensure healing progresses as expected. Patience during this period supports optimal results.
Long Term Results and Maintenance
Reconstructed breasts evolve naturally with the body. Implant based reconstruction after mastectomy may require future review depending on individual circumstances. Autologous tissue adapts with weight fluctuations and ageing. Maintaining stable body weight supports consistent appearance. Regular medical check ups remain important. With modern techniques, results can be durable and proportionate for many years.
Why Many Patients Choose Turkey for Mastectomy Reconstruction
Turkey has developed strong expertise in reconstructive surgery. Multidisciplinary teams coordinate oncology and aesthetic planning seamlessly. Advanced imaging tools assist preoperative assessment. Patients often value personalised consultations and comprehensive care pathways. Mastectomy reconstruction in Turkey combines medical precision with aesthetic sensitivity. The focus remains on restoring balance and confidence in a structured, supportive environment.
Preoperative Evaluation and Multidisciplinary Planning
Successful reconstruction after mastectomy begins long before surgery. A detailed preoperative assessment ensures that reconstruction aligns with both medical and aesthetic needs. Surgeons review overall health, skin condition and previous treatments. In many cases, oncology specialists and reconstructive surgeons collaborate closely. This multidisciplinary planning helps coordinate timing and technique. Imaging may be used to assess chest wall structure and remaining tissue. These steps allow reconstruction after mastectomy to be tailored precisely rather than approached generically.
Skin Sparing and Nipple Sparing Techniques
Modern mastectomy techniques often preserve as much natural skin as possible. Skin sparing approaches remove breast tissue while maintaining the external envelope. This creates a more natural foundation for reconstruction after mastectomy. In selected cases, nipple sparing procedures are also possible. Preserving the nipple can enhance overall aesthetic outcome and reduce the number of reconstructive stages. Careful patient selection determines suitability. These advancements have significantly improved visual and structural results.
Role of Tissue Expanders in Staged Mastectomy Reconstruction
In implant based reconstruction after mastectomy, tissue expanders are frequently used as a temporary step. These devices are placed beneath the skin and gradually filled over several weeks. The process gently stretches tissue to accommodate a permanent implant. This staged approach allows the body to adjust gradually. It also provides flexibility in determining final size. Many patients appreciate the ability to monitor shape development before implant exchange. Tissue expanders remain an important tool in structured reconstruction planning.
Abdominal Flap Reconstruction Techniques
Autologous reconstruction often utilises abdominal tissue. Procedures such as the DIEP flap transfer skin and fat while preserving muscle integrity. This technique maintains abdominal strength while creating natural breast volume. Mastectomy reconstruction using abdominal tissue often provides soft contour and long term durability. Additionally, patients benefit from improved abdominal shaping. Recovery may require additional healing time, but the outcome integrates seamlessly with the body’s tissue.
Back Based Reconstruction Options
When abdominal tissue is not suitable, surgeons may consider tissue from the back. The latissimus dorsi flap transfers muscle and skin to rebuild breast contour. In some cases, this is combined with an implant for added volume. Reconstruction after mastectomy using back tissue provides reliable blood supply and predictable healing. It is particularly useful for patients with previous abdominal surgery.
Conclusion
Mastectomy reconstruction offers multiple options tailored to individual needs. From implant based solutions to autologous tissue techniques, the process is highly personalised. Timing, anatomy and lifestyle all influence the chosen pathway. Modern surgical methods prioritise natural contour, symmetry and long term stability. With careful planning and experienced guidance, reconstruction after mastectomy can restore both physical form and personal confidence.
For more information and to book a consultation visit the ACIBADEM Beauty Center Breast Augmentation webpage.
Frequently Asked Questions
Implants use silicone devices for volume, while tissue reconstruction uses your own body tissue.
Yes, delayed reconstruction is possible even many years later.
Recovery time varies by technique, ranging from weeks to several months.
Modern techniques aim to achieve natural shape and proportion.
It can be performed as a final stage to complete overall appearance.