Introduction
Breast development varies greatly from person to person. In some cases, the breast base remains narrow during puberty. This can lead to a condition known as tubular breasts. The shape often appears elongated with limited lower fullness. Tubular breast correction focuses on reshaping and expanding the breast base. The goal is natural proportion rather than dramatic enlargement. Modern techniques now allow refined, tailored outcomes. With careful planning, tubular correction can restore balance and symmetry.
Understanding Tubular Breast Anatomy
Tubular breasts typically present with a constricted base. The lower pole may lack adequate volume. In some cases, the areola appears widened or protruding. This structure develops during early breast growth. The tissue does not fully expand across the chest wall. Tubular correction addresses these structural limits directly. Treatment focuses on releasing tight tissue and redistributing volume. Accurate diagnosis guides surgical planning from the beginning.
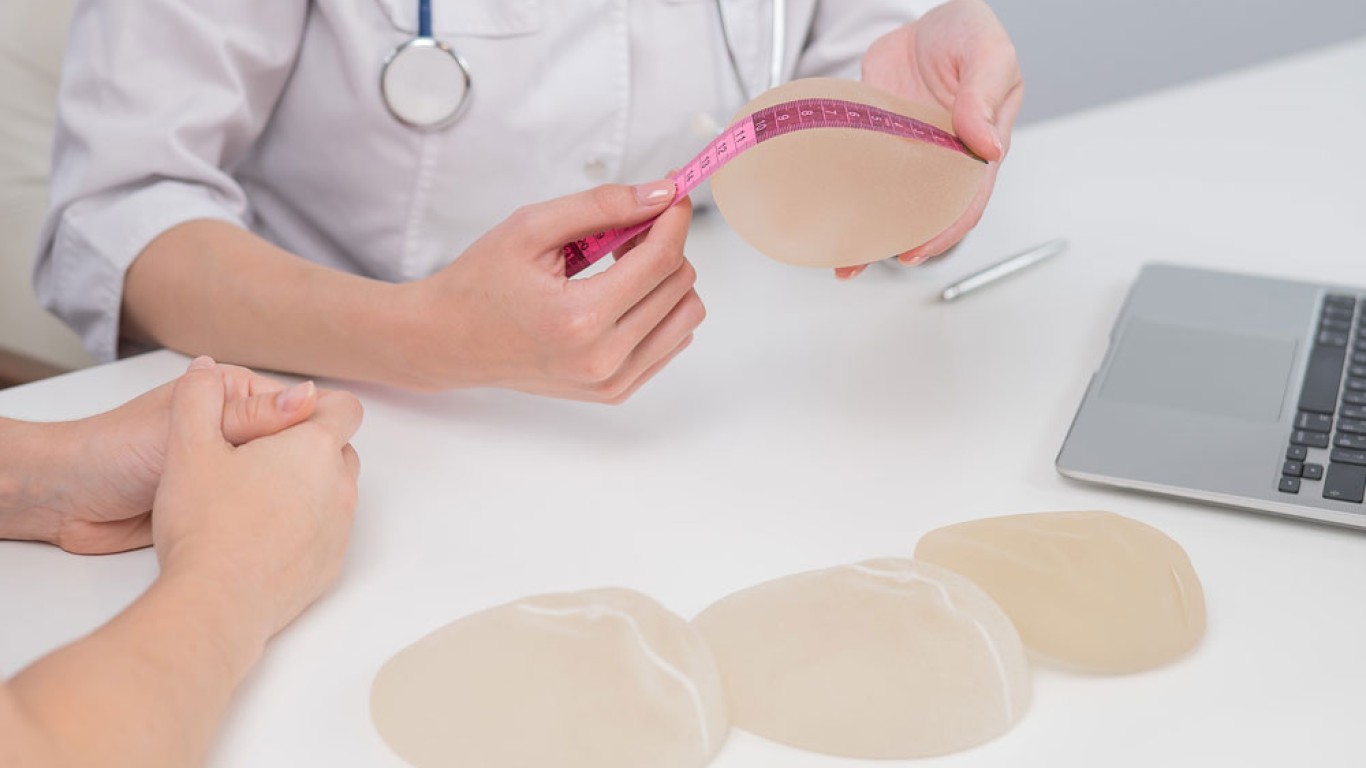
Assessment and Personalised Surgical Planning
Every case differs in severity and structure. Some women have mild asymmetry. Others present with more pronounced constriction. Tubular correction begins with detailed anatomical assessment. Surgeons evaluate base width, skin elasticity and nipple position. Digital imaging may assist in visualising expected changes. Planning ensures proportion suits the patient’s frame. Precision at this stage shapes final harmony.
Tissue Expansion and Base Release Techniques
One key step involves releasing constricted lower tissue. Tight internal bands are carefully divided. This allows the breast base to expand naturally. Tubular correction often requires reshaping internal support. By releasing the lower pole, volume can settle more evenly. The breast gains roundness without excessive projection. Modern techniques prioritise gradual contour improvement rather than overfilling.
Use of Implants in Tubular Breast Correction
In many cases, implants support reshaping. The implant helps expand the lower breast area. However, size selection remains conservative. Correction of tubular breasts does not focus solely on enlargement. Instead, implants restore balance and structure. Moderate projection typically produces the most natural result. Careful pocket creation ensures the implant integrates smoothly.
Fat Transfer as an Adjunct Technique
Fat grafting can refine contour further. This method uses the patient’s own fat to soften transitions. It can improve symmetry and enhance lower fullness. Tubular correction sometimes combines implants with fat transfer. The implant provides structure while fat adds subtle shaping. This layered approach creates smoother outlines. The final result appears cohesive rather than augmented.
Areola Reduction and Nipple Repositioning
Tubular breasts may involve enlarged areolae. Reshaping the areola can significantly improve appearance. Excess tissue is carefully reduced and repositioned. Tubular breast correction frequently includes this step. Adjusting nipple placement enhances overall proportion. Even small refinements can change the visual balance. The breast appears more centred and harmonious.
Addressing Asymmetry in Tubular Breast Correction
Asymmetry is common with tubular development. One breast may be more constricted than the other. Surgical correction accounts for these differences individually. Tubular correction may involve varying implant sizes. Tissue release may also differ between sides. Tailoring each breast separately improves symmetry. Balance remains the guiding principle throughout the procedure.
Recovery and Settling After Surgery
Initial swelling is expected after surgery. Over several weeks, the breasts begin to soften and settle. The lower pole gradually adopts a rounder contour. Correction of tubular breast results become clearer after healing progresses. Supportive garments assist during early recovery. Most patients resume daily routines within a few weeks. Final shape continues refining over several months.
Why Turkey Is a Leading Destination for Tubular Breast Correction
Turkey has become known for advanced aesthetic surgery. Surgeons combine structural understanding with modern technology. Tubular breast correction in Turkey often benefits from detailed preoperative planning. Digital simulations support realistic expectations. Surgical techniques emphasise natural proportion. Many patients value the tailored, measured approach.
Long Term Results and Natural Proportion
The aim of tubular breast correction is structural harmony. Once constricted tissue is released, the breast maintains its new base. Implants or fat grafts integrate within the reshaped framework. Over time, the breasts soften and feel natural. Proportion rather than size defines long term success. With thoughtful technique, results remain balanced and refined.
Grades of Tubular Breast Development
Tubular breast development varies in severity. Some cases involve mild lower pole constriction. Others present with significant narrowing and limited tissue expansion. Surgeons often classify the condition into different grades. Mild cases may require subtle reshaping only. More advanced forms may involve base expansion and structural support. Correction of tubular breasts are adapted according to this grading. Understanding severity helps set realistic expectations. It also determines whether implants, fat grafting or combined techniques are required. Accurate classification ensures balanced correction rather than unnecessary enlargement.
Lower Pole Expansion and Internal Scoring
A defining feature of tubular breasts is restricted lower pole growth. The lower portion appears tight and underdeveloped. This creates a high breast fold and elongated shape. Tubular breast correction often includes internal scoring techniques. These small controlled releases allow tissue to expand more naturally. Once the constriction is eased, the breast can assume a rounder contour. Lower pole expansion is central to achieving natural proportion. Without this step, volume alone would not correct the shape. Structural adjustment ensures lasting balance.
Repositioning the Inframammary Fold
The inframammary fold defines the natural crease beneath the breast. In tubular cases, this fold may sit higher than expected. That position limits lower pole fullness. Correction of tubular breasts may involve lowering this fold carefully. Adjusting its position creates space for improved contour. When the fold aligns correctly, the breast appears fuller and more proportionate. This step requires precise measurement. Even small adjustments can significantly influence final symmetry.
Choosing Implant Shape in Tubular Breast Correction
Implant selection in tubular cases differs from standard augmentation. The goal is structural support rather than dramatic size increase. Moderate profile implants are often preferred. They provide base expansion without excessive projection. Tubular correction prioritises width and contour over forward fullness. Anatomical implants may suit certain patients. Round implants can also work effectively when combined with tissue release.
Skin Management and Envelope Adjustment
Skin plays a crucial role in final appearance. In tubular breasts, the skin envelope may be tight in some areas and stretched in others. Correction of tubular breasts addresses this imbalance carefully. Minor skin tightening may accompany areola reduction. In other cases, reshaping alone improves surface contour.
Symmetry Planning in Complex Cases
Many patients with tubular breasts experience asymmetry. One side may show greater constriction or a different fold position. Tubular breast correction is planned individually for each breast. Implant size, tissue release and fold adjustment may vary side to side. This tailored approach improves visual balance. True symmetry means both breasts complement each other naturally.
Conclusion
Tubular breast correction addresses structural differences rather than simple volume concerns. By releasing constricted tissue and reshaping the lower pole, surgeons restore proportion. Modern techniques allow subtle integration of implants or fat grafting when required. Each procedure is tailored to the individual’s anatomy. The focus remains on balance, symmetry and natural contour. With experienced planning, correction of tubular breasts can transform shape while preserving authenticity.
For more information and to book a consultation visit the ACIBADEM Beauty Center Breast Augmentation webpage.
Frequently Asked Questions
Tubular breasts develop during puberty when the breast base fails to expand fully.
Not always. Some cases use fat transfer or reshaping alone.
Areola reduction is often included to improve proportion and balance.
Initial swelling settles within weeks, but final contour refines over months.
Yes, the procedure can be tailored to address individual differences on each side.