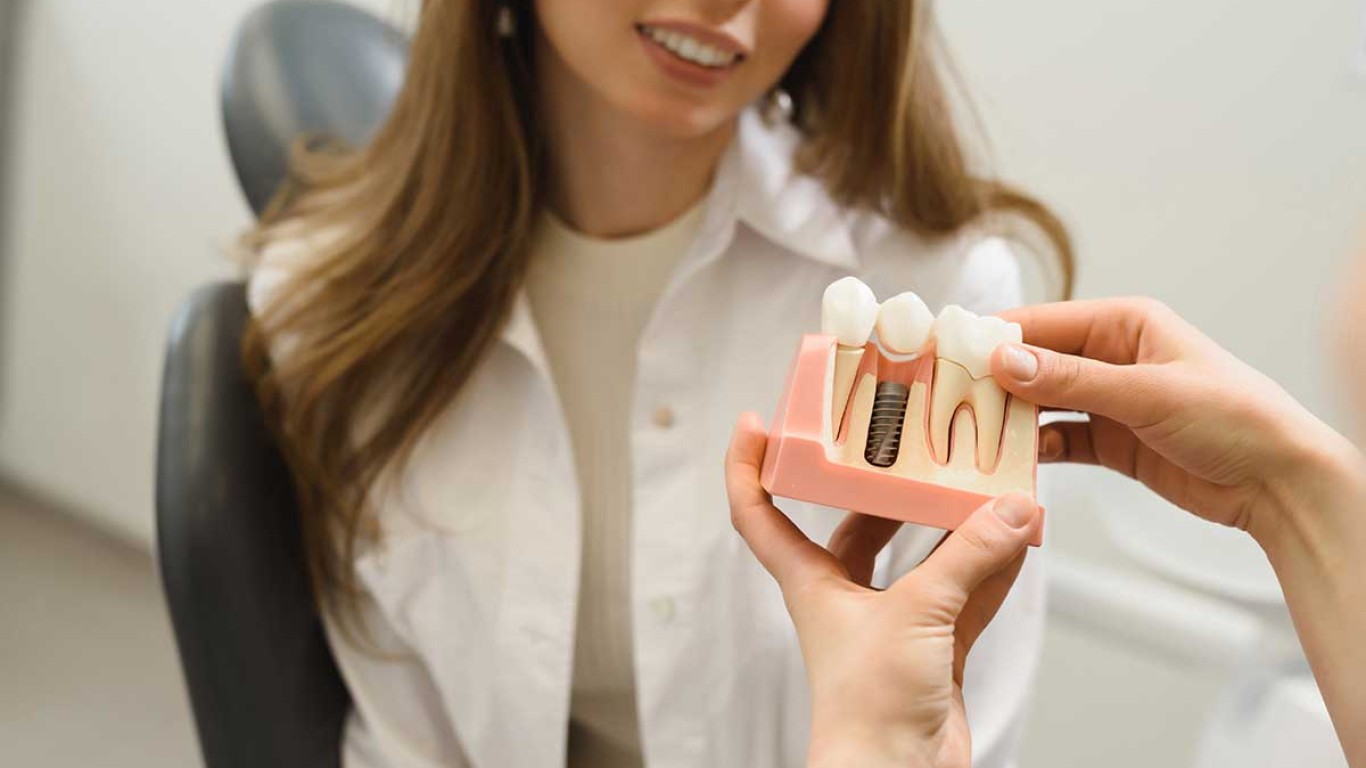
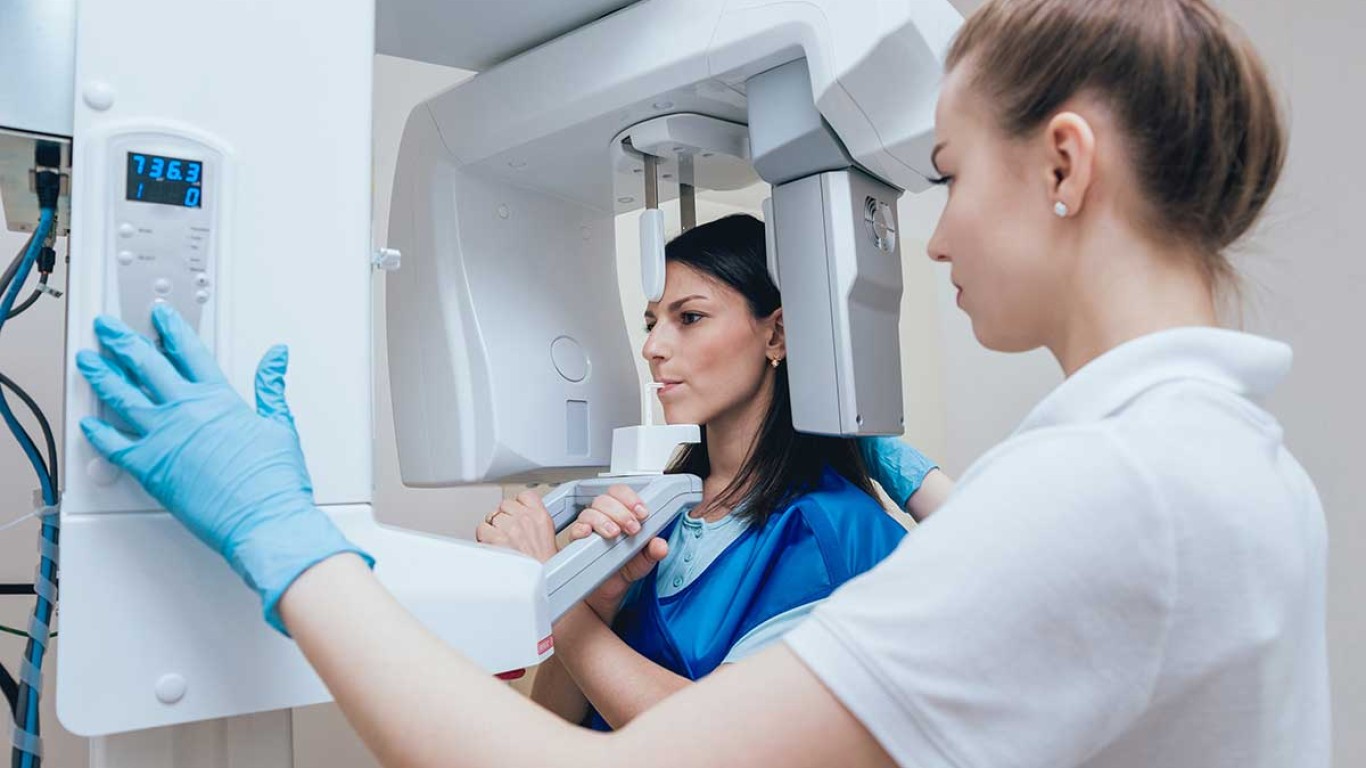
Understanding the difference between zygomatic implants vs mini dental implants helps individuals choose the most suitable solution for missing teeth. Both options restore stability, yet they serve very different needs. Zygomatic implants anchor into the cheekbone for advanced support. While mini dental implants suit narrow spaces or limited bone. This guide explains how each method works and how dentists assess suitability. Learn which approach aligns with different levels of bone structure.
What Zygomatic Implants Are Designed For
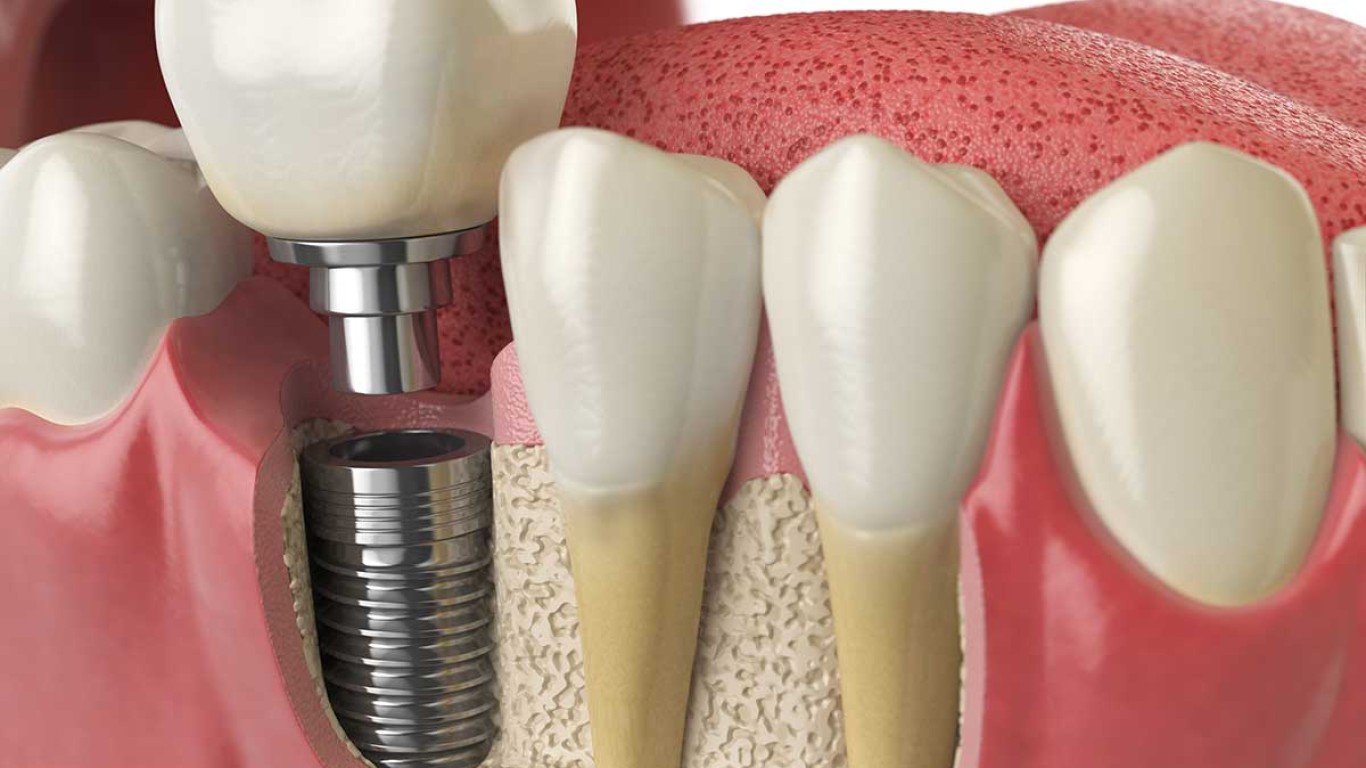
Zygomatic implants support cases of advanced upper jaw bone loss. They anchor into the zygomatic bone, which offers strong density. Because they bypass the need for upper jaw bone, they remain suitable for full arch solutions. Dentists choose this option when traditional implants cannot be placed due to limited bone.
What Mini Dental Implants Are Designed For
Mini dental implants suit individuals with narrow jaw areas or limited bone width. They feature a smaller diameter than traditional implants. This design allows placement in areas where space or bone structure may be reduced. They often support small restorations or stabilise dentures.
Comparing Purpose: Zygomatic Implants vs Mini Dental Implants
The purpose differs significantly. Zygomatic implants address severe bone loss and full arch stability. Mini dental implants support narrow gaps and denture retention. Therefore purpose and bone structure guide the choice between zygomatic implants vs mini dental implants.
How Zygomatic Implants Are Placed
Placement begins with detailed imaging and planning. Dentists map the cheekbone with 3D scans. The implant is angled through the upper jaw to anchor into the zygomatic bone. This strong anchor supports a full arch bridge. Planning ensures correct angle and depth.
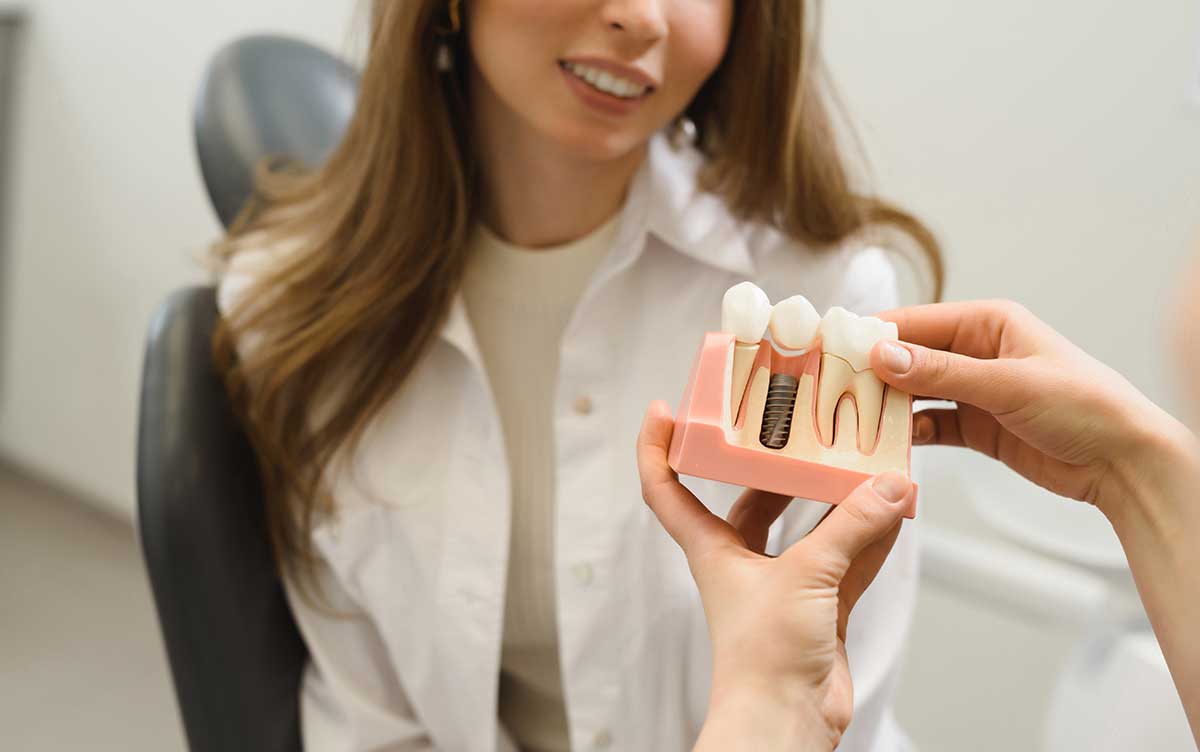

How Mini Dental Implants Are Placed
Mini dental implants use a simpler placement pathway. They are positioned directly into narrow bone areas. Their smaller diameter requires less preparation. Dentists often place several for denture support or small restorations. AI modelling helps determine spacing and direction.
Bone Structure Requirements Zygomatic Implants vs Mini Dental Implants
Zygomatic implants rely on cheekbone density. They suit individuals with major upper jaw loss. Mini dental implants require adequate bone height but less width. They suit narrower ridges. Therefore bone structure strongly influences which option fits better.
Which Patients Benefit Most From Zygomatic Implants vs Mini Dental Implants
Zygomatic implants suit individuals with severe bone loss who want fixed full arch support. They also suit those who cannot undergo complex bone reconstruction. Because they anchor into the cheekbone, they offer reliable long-term stability. Specialists recommend them for advanced reconstruction needs.
Mini dental implants suit individuals with narrow gaps, small spaces, or denture stability needs. They often support those who require immediate improvement in denture hold. Additionally, they suit those unable to receive larger implant models due to limited ridge width.
Treatment Planning for Zygomatic Implants vs Mini Dental Implants
Zygomatic planning includes 3D imaging, AI mapping, and pathway simulation. Dentists measure bone density and structural angles. Because placement requires precision, digital tools help refine direction. Specialists also evaluate bite alignment to support restoration design.
Mini Dental Implant planning includes bone width analysis and spacing evaluation. AI tools measure jaw contours and highlight ideal insertion points. Because these implants are smaller, they often require less structural preparation. Planning supports even distribution for denture stability.
How Technology Enhances Both Implant Types
Modern dentistry uses AI, digital scanning, and guided planning. Zygomatic pathways rely heavily on imaging depth. Mini dental implants benefit from spacing maps and alignment checks. Technology helps both methods achieve high accuracy.
Conclusion
Comparing zygomatic implants vs mini dental implants highlights two solutions with distinct purposes. Zygomatic implants support severe upper jaw bone loss using cheekbone anchoring. Mini dental implants suit narrow gaps and denture stability. Digital imaging, AI mapping, and structured planning help specialists choose the most suitable approach based on bone structure, restoration needs, and long-term goals.
For more information and to book a consultation visit the ACIBADEM Beauty Center Dental Treatments webpage.
Frequently Asked Questions
Zygomatic Implants anchor into the cheekbone, while Mini Dental Implants fit narrow areas.
Those with severe upper jaw bone loss and full arch needs.
They stabilise dentures or fill narrow spaces.
Yes, modern planning uses AI and 3D scanning.
Yes, suitability depends on stability and assessment.