Changes in the forehead and brow region often include descending tissue and deepening lines. These developments affect the upper face structure and create visible imbalance. Two of the most commonly chosen treatments for this area are botox injections and the endoscopic brow lift. Although both target the same region, they operate in entirely different ways.
Understanding the Endoscopic Brow Lift
An endoscopic brow lift is a surgical procedure that lifts and repositions the tissues of the forehead and brow. Instead of a long incision, the endoscopic technique uses small openings hidden in the hairline. A thin camera guides the surgeon beneath the skin to access deeper structures. The procedure focuses on releasing key ligaments, adjusting muscle activity, and repositioning tissue without tension. This deeper structural correction allows the brow to sit higher and more naturally aligned. It also modifies the forehead’s deeper planes rather than the surface only.
Understanding Botox for Brow Position and Lines
Botox is a neuromodulator injected into specific muscles to reduce movement. When used in the upper face, it relaxes the muscles responsible for forehead lines. Reducing muscle pull can achieve a mild lifting effect. Because botox affects muscle function, it remains one of the most common non-surgical approaches. However, it does not reposition deep tissues or adjust structural support. Instead, it reduces visible lines created by repetitive contraction.
Endoscopic Brow Lift vs Botox: Technical Differences
The main difference lies in the depth of correction.
- Botox acts on muscle activity only.
- An endoscopic brow lift acts on tissues, ligaments, and muscle structure.
Botox works chemically through neuromuscular blockade. The surgical lift works mechanically by releasing and repositioning underlying structures. Additionally, the endoscopic approach supports predictable anatomical change, whereas botox provides temporary functional adjustment.
Suitability Based on Age and Anatomy
Suitability depends on the extent of tissue descent, muscle pull, and skin behaviour. Individuals with early lines and mild brow heaviness generally respond well to botox. Conversely, those with structural drooping, ligament laxity, or deeper forehead descent require surgical intervention. Practitioners assess eyebrow position, forehead muscle strength, and skin elasticity before recommending a treatment. The endoscopic brow lift usually benefits those with noticeable brow descent or deeper tissue involvement.
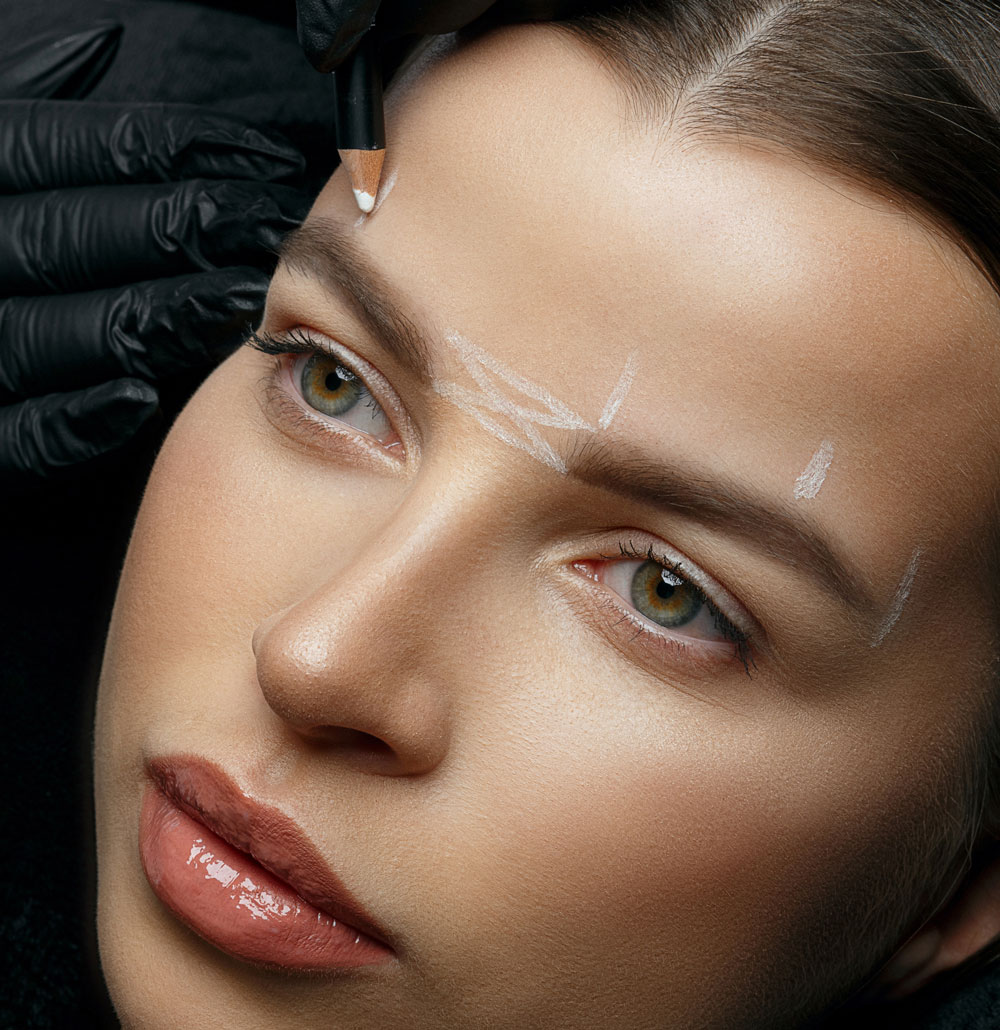

How the Endoscopic Brow Lift Is Performed
- The procedure usually takes one to two hours.
- Firstly, small incisions are made within the hairline.
- Secondly, the endoscope is inserted to allow internal visualisation.
- Thirdly, the surgeon releases specific ligaments that restrict upward movement.
- Fourthly, tissues are repositioned to a more suitable location.
- Finally, the surgeon secures the lifted tissues and closes the incisions.
This sequence ensures structural realignment without excessive skin tension.
How Botox Is Performed
Botox treatment takes minutes. The practitioner identifies active muscles, maps injection points, and administers small doses of neuromodulator. Because it only affects muscle activity, no incisions are needed.Precise placement is important because brow position depends on coordinated muscle function. Results develop within several days as the neuromodulator takes effect.
Endoscopic Brow Lift vs Botox: Result Duration
An endoscopic brow lift offers long-lasting structural change. Although ageing continues naturally, the repositioned tissues maintain improved support for many years. Botox results last three to five months. Because the effect fades as the neuromodulator wears off, repeat sessions are required. These differences allow specialists to tailor treatment based on patient goals and long-term planning.
Endoscopic Brow Lift vs Botox: Recovery Times Compared
Recovery after an endoscopic brow lift involves swelling and tightness for several days. Most patients resume light activity after one to two weeks. Because the incisions are small and placed within the hairline, they remain discreet. Botox requires no downtime. Normal activity can continue immediately because no tissue repositioning occurs. This contrast helps determine which approach suits a patient’s schedule and tolerance for recovery.
Strengths of the Endoscopic Technique
The endoscopic approach provides several structural advantages:
- It lifts deeper tissues, not only the skin.
- It reduces muscle tension through precise adjustment.
- It preserves natural hairline appearance.
- It improves brow position through ligament release.
These factors make the endoscopic brow lift suitable for structural correction.
Strengths of Botox Treatment
Botox offers flexibility because dosage can be adjusted. It also supports targeted treatment for specific lines. Such as horizontal forehead lines or glabellar frown lines. Additionally, it allows gradual refinement because adjustments can be made during follow-up appointments. It remains an effective first-line approach for those not ready for surgery.
When Both Treatments Are Combined
Many treatment plans use both methods together. The surgical lift corrects structural descent while botox controls muscle pull. This combined approach maintains improved brow position and reduces strain on lifted tissues. In 2025, combination planning has become increasingly common. Due to detailed imaging systems that map muscle activity and tissue depth before treatment.
The Role of Technology in Deciding Between Both Options
Clinics now use AI imaging and digital analysis to assess forehead movement patterns. As well as ligament behaviour, and brow angles. These tools support accurate diagnosis and help determine whether the issue is structural or functional. If ligament tension or tissue descent is detected, the endoscopic brow lift is usually recommended. If muscle activity is the primary concern, botox may be more appropriate.
Long-Term Maintenance
Maintenance differs significantly. A surgical lift requires no routine repetition, although natural ageing continues. Botox requires repeat sessions to maintain muscle control. Patients often use botox after surgery to support the internal lift. Also to reduce muscle strain on recently corrected tissues.
Conclusion
Choosing between botox and an endoscopic brow lift depends on whether the concern is muscle-related or structural. Botox suits early lines and mild descent, whereas the surgical approach corrects deeper anatomical changes. Imaging tools, accurate assessment, and clear understanding of each technique support appropriate treatment planning.
For more information and to book a consultation visit the ACIBADEM Beauty Center skin treatments webpage.
Frequently Asked Questions
It offers long-lasting structural improvement due to deeper tissue repositioning.
Botox usually lasts three to five months.
Yes, combining them improves brow stability and muscle balance.
Incisions are small and usually hidden within the hairline.
Botox suits early functional changes caused by muscle movement.